General Information
Cases/Enablers
OOP Case
Appetizer
The Estonian Medical Digital Images Bank is a central database that stores almost all of radiological images and films. Every radiologist and physician can have access to their patients` images by using ID cards.
Short summary
The Estonian Medical Digital Images data repository was established in 2005. The Medical Digital Images Bank is integrated with the Estonian Health Information System. This is a central database that stores almost all (90%) radiological images and films (MRT, CT, EKG, X-ray etc). The Images Bank is integrated with the Health Care Providers systems via a secure channel VPN. Every radiologist and physician can have access to their patients` images by using ID cards. Consequently this system gives the possibility to have the overview and dynamics during a longer period of patient history and to compare developments. It also gives the possibility to have a second opinion without making new images (and radiation). Doctors can consult each other without additional research and patient movement. The system is a very good tool for distance consultation in Estonia.
The database has a possibility for each image to have a radiologist`s prescribed answer about findings (nearly 40% have radiologists prescriptions). The same data can also be viewed by the physician or other doctors (via VPN or HIS MISP portal) who have sent the patients to the radiology examination. As the health care providers systems are integrated to the Image Bank, a radiologist has access to the Bank from every secure system and he can give answers about the images. If necessary, you can also ask for a second opinion of the same image. This allows radiologists to give answers about the images even outside of Estonia or a particular medical institution. It allows radiologists to use resources flexibly in smaller hospitals and regions. The Digital Images Repository meets international standards as DICOM and HL7.
The database has a possibility for each image to have a radiologist`s prescribed answer about findings (nearly 40% have radiologists prescriptions). The same data can also be viewed by the physician or other doctors (via VPN or HIS MISP portal) who have sent the patients to the radiology examination. As the health care providers systems are integrated to the Image Bank, a radiologist has access to the Bank from every secure system and he can give answers about the images. If necessary, you can also ask for a second opinion of the same image. This allows radiologists to give answers about the images even outside of Estonia or a particular medical institution. It allows radiologists to use resources flexibly in smaller hospitals and regions. The Digital Images Repository meets international standards as DICOM and HL7.
Focus
Citizens
Start date
Domain
Health
Scope
National/Federal
Country
Estonia
Nature and status of project
Rolled Out
Is the OOP case/enabler mandatory?
Opt-in
ENABLING ASSETS OR COMPONENTS
Relevant Enablers
Legal interoperability
Health Services Organisation Act, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/513032017001/consolide
------------
National Health Information System Regulation, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/akt/106122016011
------------
Personal Data Protection Act, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/akt/12805972?leiaKehtiv
------------
Population Register Act, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/523032017001/consolide
------------
Public Information Act, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/518012016001/consolide
------------
National Health Information System Regulation, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/akt/106122016011
------------
Personal Data Protection Act, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/akt/12805972?leiaKehtiv
------------
Population Register Act, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/523032017001/consolide
------------
Public Information Act, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/518012016001/consolide
Socio-cultural influence factors
Legal and organizational interoperability: legislation approved by stakeholders
All registers must linked by use commonly accepted keys:
• personal code for citizens,
• code of institution,
• standardized address presentation.
Secure data exchange via VPN
All participants must be implemented three-level IT baseline security system ISKE (https://www.ria.ee/en/iske-en.html). The goal of implementing ISKE is to ensure a security level sufficient for the data processed in IT systems. The necessary security level achieved by implementing the standard organizational, infrastructural/physical and technical security measures.
Data guidelines of Estonian Data Protection Inspectorate (http://www.aki.ee/et/juhised) must followed.
All registers must linked by use commonly accepted keys:
• personal code for citizens,
• code of institution,
• standardized address presentation.
Secure data exchange via VPN
All participants must be implemented three-level IT baseline security system ISKE (https://www.ria.ee/en/iske-en.html). The goal of implementing ISKE is to ensure a security level sufficient for the data processed in IT systems. The necessary security level achieved by implementing the standard organizational, infrastructural/physical and technical security measures.
Data guidelines of Estonian Data Protection Inspectorate (http://www.aki.ee/et/juhised) must followed.
DATA HANDLING / DATA EXCHANGE
Type of data sharing
Actual data
Data handler
Stakeholder name
Medical Digital Images Bank (PACS Repository)
Stakeholder category
Business
Stakeholder Role
Data provider
Kind of data
Health data
Stakeholder name
Health Information System (TEHIK)
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data provider
Kind of data
Health data
Stakeholder name
Population Register
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data provider
Kind of data
Health data
Stakeholder name
Business Register
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data provider
Kind of data
Health data
Stakeholder name
Citizen
Stakeholder category
Citizen
Stakeholder Role
Data consumer
Kind of data
Health data
Stakeholder name
Health Care providers (GP, Hospital, Dentists)
Stakeholder category
Business
Stakeholder Role
Data recorder
Kind of data
Health data
Stakeholder name
Health care providers Register (Health care Board)
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data provider
Kind of data
Health data
Stakeholder name
Health professionals Register (Health care Board)
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data provider
Kind of data
Health data
Stakeholder name
HIS X-Road MISP – Portal for GP
Stakeholder category
Business
Stakeholder Role
Data consumer
Kind of data
Health data
Stakeholder name
State Information Board (eID, Mobile-ID, ID-card)
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data supervisor
Kind of data
Health data
Image upload
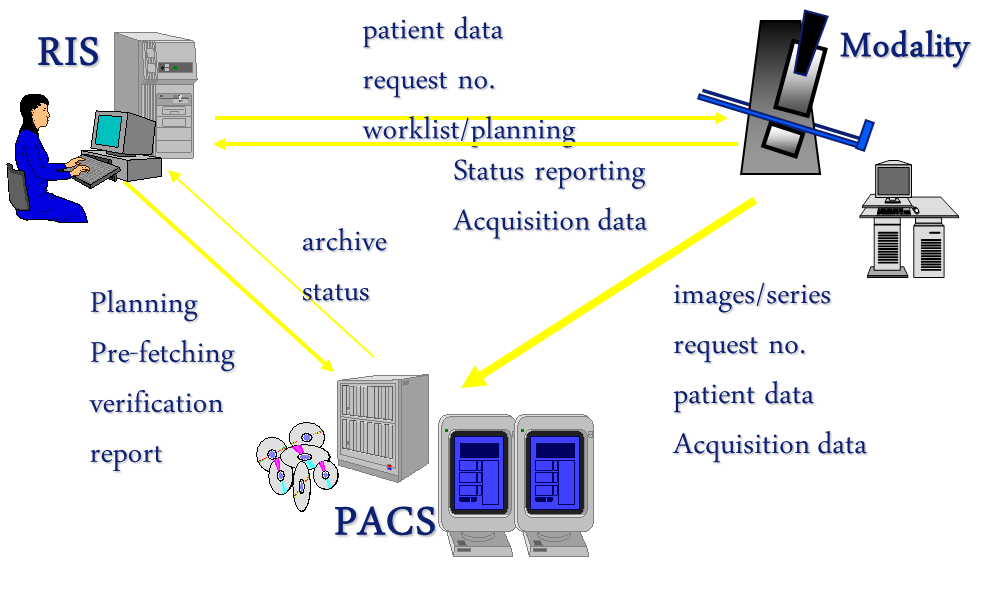
Lessons learned
Benefits:
- Each attending doctor is able to see whether ordered test results are in, even if the tests were made by another provider
- Reduced number of duplicate tests for the same case
- Makes available the distance consultation without patient movement
- Good cooperation and centralized repository gives a commercial effect (competent, hardware, logistics, services, costs)
- Radiologists in different geographic locations can make comments on radiological images in the central repository or test results in the HIS, using a secure channel (VPN)
Enablers:
• Legal, organizational, technical, social-cultural, fiscal and professional interoperability
• Secure data exchange (ISKE, VPN, encrypted data, access by ID card)
• Organizational and leaders understanding about cooperation benefits (increased handling costs and readiness for integration of medical equipment)
• Used international standards like DICOM and HL7 (because of medical devices)
• All health care providers have a contract with the Digital Images Bank
• Transparent pricing – same price for all counterparts. Every achieving costs
Barriers :
All Medical devices don’t have yet the readiness for digital ordination and outcomes
Lack of cooperation and understanding
Lacking of digital ordering services among the health care providers
High development costs (speed, size, security and availability)
- Each attending doctor is able to see whether ordered test results are in, even if the tests were made by another provider
- Reduced number of duplicate tests for the same case
- Makes available the distance consultation without patient movement
- Good cooperation and centralized repository gives a commercial effect (competent, hardware, logistics, services, costs)
- Radiologists in different geographic locations can make comments on radiological images in the central repository or test results in the HIS, using a secure channel (VPN)
Enablers:
• Legal, organizational, technical, social-cultural, fiscal and professional interoperability
• Secure data exchange (ISKE, VPN, encrypted data, access by ID card)
• Organizational and leaders understanding about cooperation benefits (increased handling costs and readiness for integration of medical equipment)
• Used international standards like DICOM and HL7 (because of medical devices)
• All health care providers have a contract with the Digital Images Bank
• Transparent pricing – same price for all counterparts. Every achieving costs
Barriers :
All Medical devices don’t have yet the readiness for digital ordination and outcomes
Lack of cooperation and understanding
Lacking of digital ordering services among the health care providers
High development costs (speed, size, security and availability)
