General Information
Cases/Enablers
OOP Case
Appetizer
The Estonian Parental benefit service is a one click service for parents to apply for the benefit. To apply for the parental benefit, an application must be submitted via the State Portal or at a regional bureau of the Social Insurance Board.
Short summary
To apply for the parental benefit, an application must be submitted via the State Portal or at a regional bureau of the Social Insurance Board. The benefit will start to be paid one day after the period for paying maternity benefit or adoption benefit. Those who do not receive the maternity benefit are paid the parental benefit starting from the birth of the child. The childcare benefit is not paid to parents who receive the parental benefit. Income tax is withheld from the parental benefit.
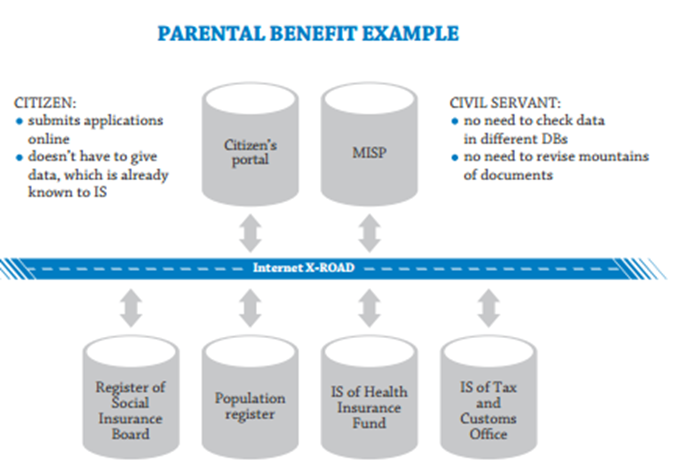
Citizen can apply for the parental benefit at the Social Insurance Board. The Social Insurance Board officers obtain the data they require from different databases.
The Estonian Parental benefit service is a one click service for parents to apply for the benefit.
Citizen can apply for the parental benefit at the Social Insurance Board. The Social Insurance Board officers obtain the data they require from different databases.
The Estonian Parental benefit service is a one click service for parents to apply for the benefit.
Focus
Citizens
Start date
Domain
Social matter
Scope
National/Federal
Country
Estonia
Nature and status of project
Rolled Out
Is the OOP case/enabler mandatory?
Opt-in
ENABLING ASSETS OR COMPONENTS
Relevant Enablers
Political commitment
Interoperability of the State Information System. Endorsed with the Directive of the Minister of Economic Affairs and Communications 11-0377, 22.12.2011, https://www.mkm.ee/sites/default/files/interoperability-framework_2011.doc
Legal interoperability
Parental Benefit Act. Riigikogu. RT I 2003, 82, 549, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/ee/528122016010/consolide/current
----------
Health Insurance Act. Riigikogu. RT I 2002, 62, 377, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/529122016002/consolide
----------
Income Tax Act. Riigikogu. RT I 1999, 101, 903, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/516012017002/consolide
----------
Health Insurance Act. Riigikogu. RT I 2002, 62, 377, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/529122016002/consolide
----------
Income Tax Act. Riigikogu. RT I 1999, 101, 903, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/516012017002/consolide
Socio-cultural influence factors
Parental benefit procedures are supported by Parental Benefit Act and by strategical documents of Ministry of Social Affairs.
All registers must linked by use personal code for citizens.
Secure data exchange layer X-Road (https://www.ria.ee/en/x-road.html) is used for gathering data from different registers. X-Road is a technological and organizational environment enabling a secure Internet-based data exchange between information systems. All registers and Statistics Estonia must be a member of X-Road
Information regarding the X-Road members and the services they provide is available via the Administration System for the State Information System (RIHA). RIHA (https://www.ria.ee/en/administration-system-of-the-state-information-system.html ) serves as a catalogue for the state’s information system. At the same time RIHA is a procedural and administrative environment via which the comprehensive and balanced development of the state’s information system is ensured. RIHA guarantees the transparency of the administration of the state’s information system and helps to plan the state’s information management.
PKI or the public key infrastructure ( https://www.ria.ee/en/public-key-infrastructure.html ) enables secure digital authentication and signing. The infrastructure also allows forwarding data by using an encrypting key pair: a public encryption key and a private decryption key. In Estonia, this technology is used in relation with electronic identity (ID card, mobile ID, digital ID). All members of X-Road are using Digital seal certificates for signing messages. Citizens and officials are using electronic identity tokens.
All participants must be implemented three-level IT baseline security system ISKE (https://www.ria.ee/en/iske-en.html). The goal of implementing ISKE is to ensure a security level sufficient for the data processed in IT systems. The necessary security level is achieved by implementing the standard organisational, infrastructural/physical and technical security measures.
Data guidelines of Estonian Data Protection Inspectorate (http://www.aki.ee/et/juhised) must be followed.
All registers must linked by use personal code for citizens.
Secure data exchange layer X-Road (https://www.ria.ee/en/x-road.html) is used for gathering data from different registers. X-Road is a technological and organizational environment enabling a secure Internet-based data exchange between information systems. All registers and Statistics Estonia must be a member of X-Road
Information regarding the X-Road members and the services they provide is available via the Administration System for the State Information System (RIHA). RIHA (https://www.ria.ee/en/administration-system-of-the-state-information-system.html ) serves as a catalogue for the state’s information system. At the same time RIHA is a procedural and administrative environment via which the comprehensive and balanced development of the state’s information system is ensured. RIHA guarantees the transparency of the administration of the state’s information system and helps to plan the state’s information management.
PKI or the public key infrastructure ( https://www.ria.ee/en/public-key-infrastructure.html ) enables secure digital authentication and signing. The infrastructure also allows forwarding data by using an encrypting key pair: a public encryption key and a private decryption key. In Estonia, this technology is used in relation with electronic identity (ID card, mobile ID, digital ID). All members of X-Road are using Digital seal certificates for signing messages. Citizens and officials are using electronic identity tokens.
All participants must be implemented three-level IT baseline security system ISKE (https://www.ria.ee/en/iske-en.html). The goal of implementing ISKE is to ensure a security level sufficient for the data processed in IT systems. The necessary security level is achieved by implementing the standard organisational, infrastructural/physical and technical security measures.
Data guidelines of Estonian Data Protection Inspectorate (http://www.aki.ee/et/juhised) must be followed.
DATA HANDLING / DATA EXCHANGE
Type of data sharing
Actual data
Data handler
Stakeholder name
Social Insurance Board
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Database owner
Kind of data
Parental benefit data
Stakeholder name
Citizens
Stakeholder category
Citizen
Stakeholder Role
Data consumer
Kind of data
Parental benefit data
Stakeholder name
Public administration
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data consumer
Kind of data
Parental benefit data
Stakeholder name
Register of Social Insurance Board (STAR)
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data consumer
Kind of data
Parental benefit data
Stakeholder name
Population Register (RR)
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data provider
Kind of data
Parental benefit data
Stakeholder name
Information System of Health Insurance Fund (EHK)
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data consumer
Kind of data
Parental benefit data
Stakeholder name
IS of Tax & Customs Board (EMTA)
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data provider
Kind of data
Parental benefit data
Stakeholder name
Estonian Education Information System (EHIS)
Stakeholder Role
Data provider
Kind of data
Parental benefit data
Architecture
Data architecture
To apply for the parental benefit, an application must be submitted via the State Portal or at a regional bureau of the Social Insurance Board. The benefit will start to be paid one day after the period for paying maternity benefit or adoption benefit. Those who do not receive the maternity benefit are paid the parental benefit starting from the birth of the child. The childcare benefit is not paid to parents who receive the parental benefit. Income tax is withheld from the parental benefit.
Before the child turns 70 days of age, the mother raising the child has the right to the compensation; after that the parents have the right to the benefit by turns. The amount of the benefit is 100% of the average income for one calendar year and the benefit is calculated on the basis of the income in the calendar year prior to the day on which the right to the benefit arose. The maximum amount of the parental benefit is three times the average wage approved by the Government of the Republic. If the income for the previous year was less than the minimum monthly wage level established by the Government, the amount of the parental benefit shall be equal to the minimum monthly wage. If there was no income subject to social tax at all, the amount of the benefit is equal to the rate of the benefit. Those who did not earn income are ensured an income equal to the benefit level (390 euros in 2016).
To apply for the parental benefit, an application must be submitted via the State Portal (https://www.eesti.ee/est/teenused/kodanik/perekond_1/vanemahuvitise_peretoetuste_ja_kogumispensioni_sissemaksete_taotlemine) or at a regional bureau of the Social Insurance Board (https://www.eesti.ee/eng/contacts/valitsusasutused/riigiametid/sotsiaalkindlustusamet )
Linking registers
Resident will log in by using eID and submit Personal Identification Number. Other data will be collected from registers.
To apply for the parental benefit, an application must be submitted via the State Portal or at a regional bureau of the Social Insurance Board. The benefit will start to be paid one day after the period for paying maternity benefit or adoption benefit. Those who do not receive the maternity benefit are paid the parental benefit starting from the birth of the child. The childcare benefit is not paid to parents who receive the parental benefit. Income tax is withheld from the parental benefit.
Before the child turns 70 days of age, the mother raising the child has the right to the compensation; after that the parents have the right to the benefit by turns. The amount of the benefit is 100% of the average income for one calendar year and the benefit is calculated on the basis of the income in the calendar year prior to the day on which the right to the benefit arose. The maximum amount of the parental benefit is three times the average wage approved by the Government of the Republic. If the income for the previous year was less than the minimum monthly wage level established by the Government, the amount of the parental benefit shall be equal to the minimum monthly wage. If there was no income subject to social tax at all, the amount of the benefit is equal to the rate of the benefit. Those who did not earn income are ensured an income equal to the benefit level (390 euros in 2016).
To apply for the parental benefit, an application must be submitted via the State Portal (https://www.eesti.ee/est/teenused/kodanik/perekond_1/vanemahuvitise_peretoetuste_ja_kogumispensioni_sissemaksete_taotlemine) or at a regional bureau of the Social Insurance Board (https://www.eesti.ee/eng/contacts/valitsusasutused/riigiametid/sotsiaalkindlustusamet )
Linking registers
Resident will log in by using eID and submit Personal Identification Number. Other data will be collected from registers.
Image upload
Lessons learned
Enabler 1. Legal and organizational interoperability: legislation approved by stakeholders; government solutions pass interoperability assessment process.
Enabler 1. eID and PKI infrastructure needed. Citizen can use for login IDcard, mobileID or digiID
Enabler 2. Secure data exchange layer for confidential and legally binding data needed. In case of Estonia the X-Road is used
Enabler 3. Master data in population registers must described in catalogue RIHA properly.
Enabler 4. The unique personal identification code provide opportunity to merge personal data from different registers.
Barrier 1. Owners of registers are fixed by legislation, but it is unclear, who is responsible for development and maintenance of front end service
Barriers 2. Calculation algorithm of benefits and a set of registers needed changes frequently according to political decisions
Enabler 1. eID and PKI infrastructure needed. Citizen can use for login IDcard, mobileID or digiID
Enabler 2. Secure data exchange layer for confidential and legally binding data needed. In case of Estonia the X-Road is used
Enabler 3. Master data in population registers must described in catalogue RIHA properly.
Enabler 4. The unique personal identification code provide opportunity to merge personal data from different registers.
Barrier 1. Owners of registers are fixed by legislation, but it is unclear, who is responsible for development and maintenance of front end service
Barriers 2. Calculation algorithm of benefits and a set of registers needed changes frequently according to political decisions
