General Information
Cases/Enablers
OOP Case
Appetizer
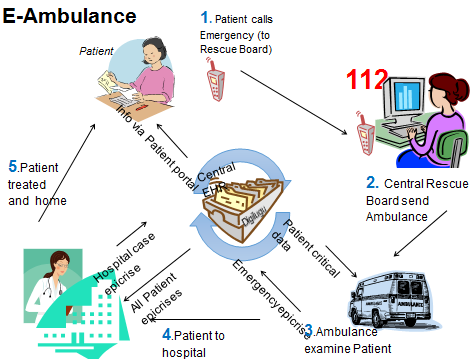
In an emergency, it is very helpful to have quick background information for patient review, especially as the patient is often unconscious. When a person is identified, time-critical data, like information about allergies, can be quickly served from a central database.
Short summary
In emergency situations (ambulance or emergency service) it is very helpful to have quick background information for patient review, especially as the patient is often unconscious. When a person is identified (personal ID–code is identified), time-critical data (allergies, past acute submissions and visits, the main diagnoses, major surgeries, medications, etc) can be quickly served from a central database. The time–critical data include allergies, last visits, the main diagnoses, major surgeries, medications, etc. The speed and quality of this service depends on the integrated solutions of the specific health care providers system.
Focus
Citizens
Start date
Domain
Health
Scope
National/Federal
Country
Estonia
Nature and status of project
Rolled Out
Is the OOP case/enabler mandatory?
Opt-in
ENABLING ASSETS OR COMPONENTS
Relevant Enablers
Political commitment
e-Health National Strategy
* http://sm.ee/en/e-health
* https://www.digilugu.ee/
* http://sm.ee/et/eesti-e-tervise-strateegia
* http://tehik.ee/
* http://sm.ee/en/e-health
* https://www.digilugu.ee/
* http://sm.ee/et/eesti-e-tervise-strateegia
* http://tehik.ee/
Legal interoperability
Health Services Organisation Act, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/513032017001/consolide
Especially Chapter 51 HEALTH INFORMATION SYSTEM (adopted on 2008)
---------
National Health Information System Regulation, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/akt/106122016011
---------
Personal Data Protection Act, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/akt/12805972?leiaKehtiv
---------
Public Information Act, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/518012016001/consolide
---------
Population Register Act, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/523032017001/consolide
Especially Chapter 51 HEALTH INFORMATION SYSTEM (adopted on 2008)
---------
National Health Information System Regulation, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/akt/106122016011
---------
Personal Data Protection Act, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/akt/12805972?leiaKehtiv
---------
Public Information Act, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/518012016001/consolide
---------
Population Register Act, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/523032017001/consolide
Socio-cultural influence factors
Legal and organizational interoperability: legislation approved by stakeholders
All registers must linked by use commonly accepted keys:
• personal code for citizens,
• code of institution,
• standardized address presentation.
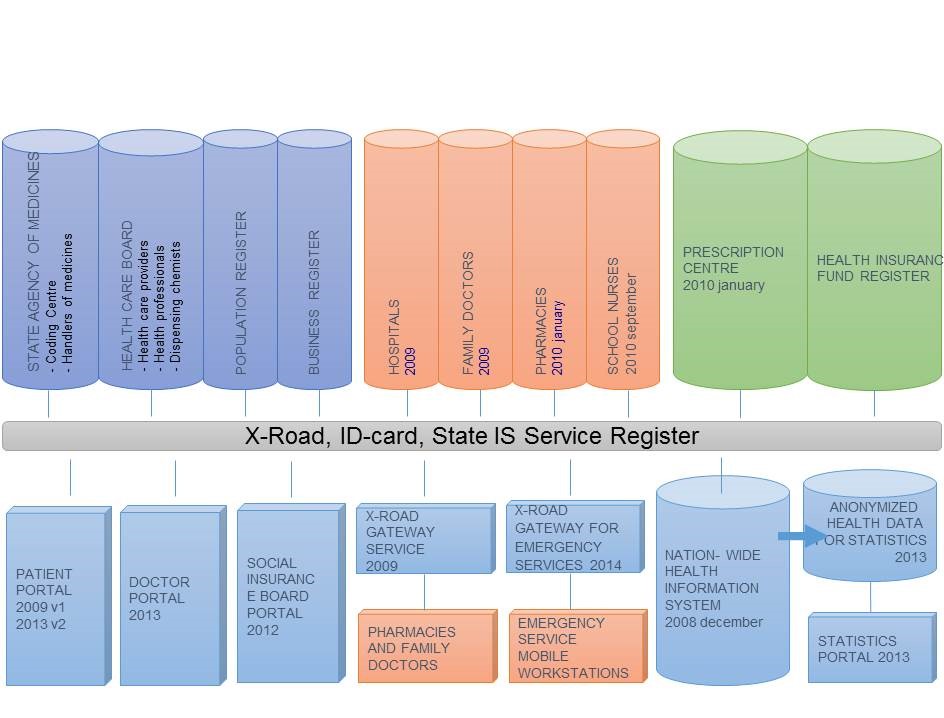
Secure data exchange layer X-Road (https://www.ria.ee/en/x-road.html) is used for gathering data from different registers. X-Road is a technological and organizational environment enabling a secure Internet-based data exchange between information systems. All registers and Statistics Estonia must be a member of X-Road
Information regarding the X-Road members and the services they provide is available via the Administration System for the State Information System (RIHA). RIHA (https://www.ria.ee/en/administration-system-of-the-state-information-system.html ) serves as a catalogue for the state’s information system. At the same time RIHA is a procedural and administrative environment via which the comprehensive and balanced development of the state’s information system has ensured. RIHA guarantees the transparency of the administration of the state’s information system and helps to plan the state’s information management.
PKI or the public key infrastructure (https://www.ria.ee/en/public-key-infrastructure.html ) enables secure digital authentication and signing. The infrastructure also allows forwarding data by using an encrypting key pair: a public encryption key and a private decryption key. In Estonia, this technology is used in relation with electronic identity (ID card, mobile ID, digital ID). All members of X-Road are using Digital seal certificates for signing messages. Citizens and officials are using electronic identity tokens.
All participants must be implemented three-level IT baseline security system ISKE (https://www.ria.ee/en/iske-en.html). The goal of implementing ISKE is to ensure a security level sufficient for the data processed in IT systems. The necessary security level achieved by implementing the standard organisational, infrastructural/physical and technical security measures.
Data guidelines of Estonian Data Protection Inspectorate (http://www.aki.ee/et/juhised) must followed.
All registers must linked by use commonly accepted keys:
• personal code for citizens,
• code of institution,
• standardized address presentation.
Secure data exchange layer X-Road (https://www.ria.ee/en/x-road.html) is used for gathering data from different registers. X-Road is a technological and organizational environment enabling a secure Internet-based data exchange between information systems. All registers and Statistics Estonia must be a member of X-Road
Information regarding the X-Road members and the services they provide is available via the Administration System for the State Information System (RIHA). RIHA (https://www.ria.ee/en/administration-system-of-the-state-information-system.html ) serves as a catalogue for the state’s information system. At the same time RIHA is a procedural and administrative environment via which the comprehensive and balanced development of the state’s information system has ensured. RIHA guarantees the transparency of the administration of the state’s information system and helps to plan the state’s information management.
PKI or the public key infrastructure (https://www.ria.ee/en/public-key-infrastructure.html ) enables secure digital authentication and signing. The infrastructure also allows forwarding data by using an encrypting key pair: a public encryption key and a private decryption key. In Estonia, this technology is used in relation with electronic identity (ID card, mobile ID, digital ID). All members of X-Road are using Digital seal certificates for signing messages. Citizens and officials are using electronic identity tokens.
All participants must be implemented three-level IT baseline security system ISKE (https://www.ria.ee/en/iske-en.html). The goal of implementing ISKE is to ensure a security level sufficient for the data processed in IT systems. The necessary security level achieved by implementing the standard organisational, infrastructural/physical and technical security measures.
Data guidelines of Estonian Data Protection Inspectorate (http://www.aki.ee/et/juhised) must followed.
DATA HANDLING / DATA EXCHANGE
Type of data sharing
Actual data
Data handler
Stakeholder name
Health Information System services – time-critical data and e-Ambulance (TEHIK)
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Database owner
Kind of data
Health data
Stakeholder name
Population Register
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data provider
Kind of data
Personal data
Stakeholder name
Business Register
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data provider
Kind of data
usiness data
Stakeholder name
Health Care providers (Emergency service, GP, Hospitals, Dentists)
Stakeholder category
Business
Stakeholder Role
Data consumer
Kind of data
Health data
Stakeholder name
Health Insurance Status Register (Health Insurance Foundation)
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data provider
Kind of data
Health data
Stakeholder name
Health care providers Register (Health care Board)
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data consumer
Kind of data
Health data
Stakeholder name
Health professionals Register (Health care Board)
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data provider
Kind of data
Semantic assets
Stakeholder name
HIS X-Road MISP – portal for Emergency Mobile Stations
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data aggregator
Kind of data
Health data
Stakeholder name
State Information Board (X-road, eID, Mobile-ID, ID-card)
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data supervisor
Kind of data
Semantic assets
Image upload
Lessons learned
Benefits:
- A brief general overview of patient’s critical data is available without any tests in emergency situations incl. in emergency medical care via mobile desks to the Ambulance and Emergency care
- Collected data can be used already in the Ambulance care on the way to patient when the ID code is detected via the rescue desk (112)
- Patient historical and current data could reuse directly to the Ambulance record and to send to the hospital if needed
Lessons learned
Enablers:
• Legal, organizational, technical, social-cultural, fiscal and professional interoperability
• The HIS architecture enables the fast collection and reusing the data (special agents collecting over the all cases the critical data)
• Wireless secure access to the data from anywhere, technical solutions
• Good cooperation with Rescue Administration, Police and the ministries of Interior and Communication and Economy
• Optimized working flow and data reusing
Barriers :
Technical equipment and secure wireless connection for mobile desks outside the hospitals (in the Ambulance car on anywhere where the patient is)
High development costs (standards, hardware, software, training)
Feasibility
- A brief general overview of patient’s critical data is available without any tests in emergency situations incl. in emergency medical care via mobile desks to the Ambulance and Emergency care
- Collected data can be used already in the Ambulance care on the way to patient when the ID code is detected via the rescue desk (112)
- Patient historical and current data could reuse directly to the Ambulance record and to send to the hospital if needed
Lessons learned
Enablers:
• Legal, organizational, technical, social-cultural, fiscal and professional interoperability
• The HIS architecture enables the fast collection and reusing the data (special agents collecting over the all cases the critical data)
• Wireless secure access to the data from anywhere, technical solutions
• Good cooperation with Rescue Administration, Police and the ministries of Interior and Communication and Economy
• Optimized working flow and data reusing
Barriers :
Technical equipment and secure wireless connection for mobile desks outside the hospitals (in the Ambulance car on anywhere where the patient is)
High development costs (standards, hardware, software, training)
Feasibility
