General Information
Cases/Enablers
OOP Enabling Infrastructure
Appetizer
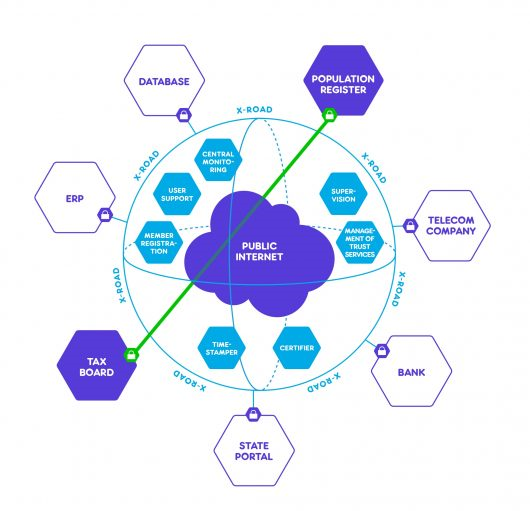
X-Road, the data exchange layer for information systems, is a technological and organizational environment enabling a secure Internet-based data exchange between information systems.
OOP aspect
X-Road is tool for secure obtining master data from systems, whish are responsible for collecting these data.
Short summary
X-Road, the data exchange layer for information systems, is a technological and organizational environment enabling a secure Internet-based data exchange between information systems.
X-Road employs a versatile security solution: authentication, multilevel authorization, a high-level log processing system, encrypted and time-stamped data traffic.
Public and private sector enterprises and institutions can connect their information system with X-Road. Joining the X-Road enables institutions to save resources, since a cooperative and secure data exchange layer already exists with all the other X-Road members. Data exchange between all the members of the X-Road ecosystem is significantly more efficient.
Indirectly, X-Road also enables citizens and officials to operate via different portals and applications (document management systems, institutional information systems) in a more efficient and flexible manner. For example, it helps checking for relevant information in national databases or securely exchange documents with institutions.
X-Road employs a versatile security solution: authentication, multilevel authorization, a high-level log processing system, encrypted and time-stamped data traffic.
Public and private sector enterprises and institutions can connect their information system with X-Road. Joining the X-Road enables institutions to save resources, since a cooperative and secure data exchange layer already exists with all the other X-Road members. Data exchange between all the members of the X-Road ecosystem is significantly more efficient.
Indirectly, X-Road also enables citizens and officials to operate via different portals and applications (document management systems, institutional information systems) in a more efficient and flexible manner. For example, it helps checking for relevant information in national databases or securely exchange documents with institutions.
Focus
Citizens
Business
NGO's
Government
Start date
Scope
Cross-border International
Country
Estonia
Finland
Nature and status of project
Rolled Out
Is the OOP case/enabler mandatory?
Mandatory
File upload
ENABLING ASSETS OR COMPONENTS
Relevant Enablers
Political commitment
Interoperability of the State Information System. Endorsed with the Directive of the Minister of Economic Affairs and Communications 11-0377, 22.12.2011.
https://www.mkm.ee/sites/default/files/interoperability-framework_2011.doc
https://www.mkm.ee/sites/default/files/interoperability-framework_2011.doc
Legal interoperability
Public Information Act. Riigikogu, RT I 2000, 92, 597, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/518012016001/consolide
---------
Personal Data Protection Act. Riigikogu, RT I 2007, 24, 127, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/507032016001/consolide
--------
The data exchange layer of information system. Vabariigi Valitsus, RT I 27.09.2016, 4, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/akt/127092016004
----------
The administration system of state information system. Vabariigi Valitsus, RT I
29.03.2016, 6, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/akt/129032016006
---------
Personal Data Protection Act. Riigikogu, RT I 2007, 24, 127, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/en/eli/507032016001/consolide
--------
The data exchange layer of information system. Vabariigi Valitsus, RT I 27.09.2016, 4, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/akt/127092016004
----------
The administration system of state information system. Vabariigi Valitsus, RT I
29.03.2016, 6, https://www.riigiteataja.ee/akt/129032016006
Organizational commitment
It exists organisatsional strructure that fix clear responsibilities for all stakeholders
Secure data exchange layer X-Road is the well proven component of Estonian IT
Secure data exchange layer X-Road is the well proven component of Estonian IT
Semantic interoperability
X-Road provides data exchange without changing it meaning
The unique personal identification code provide opportunity to merge personal data from different registers.
The unique company commercial registry code provide opportunity to merge business data from different registers.
Master data in registers and services must be described in catalogue RIHA
The unique personal identification code provide opportunity to merge personal data from different registers.
The unique company commercial registry code provide opportunity to merge business data from different registers.
Master data in registers and services must be described in catalogue RIHA
Technical interoperability
X-Road fully matches the EU conceptual model of services
Interoperability governance
Owner of X-Road is body who coordinates information systems in country. (Mnistry of Economic Affairs and Communications in Estonia). X-Road is operated by implementation body ( Information System Authority in Estonia). Service providers, intermediators and consumers are responsible for own systems
Motivations, benefits, public value
X-Road saves working time for all stakeholders
• The unique personal identification code provide opportunity to merge personal data from different registers.
• The unique company commercial registry code provide opportunity to merge business data from different registers.
• Master data in registers and services must be described in catalogue RIHA
• The unique personal identification code provide opportunity to merge personal data from different registers.
• The unique company commercial registry code provide opportunity to merge business data from different registers.
• Master data in registers and services must be described in catalogue RIHA
Data protection and privacy
X-Road supports highest data protection and privacy requirements of EIDAS and GDPR
Trust and transparency
X-Road supports highest level trust and transparency requirements
Socio-cultural influence factors
All registers must linked by use commonly accepted keys:
• personal code for citizens,
• code of institution,
• standardised address presentation.
Information regarding the X-Road members and the services they provide is available via the Administration System for the State Information System (RIHA). RIHA (https://www.ria.ee/en/administration-system-of-the-state-information-system.html ) serves as a catalogue for the state’s information system. At the same time RIHA is a procedural and administrative environment via which the comprehensive and balanced development of the state’s information system has ensured. RIHA guarantees the transparency of the administration of the state’s information system and helps to plan the state’s information management.
PKI or the public key infrastructure (https://www.ria.ee/en/public-key-infrastructure.html ) enables secure digital authentication and signing. The infrastructure also allows forwarding data by using an encrypting key pair: a public encryption key and a private decryption key. In Estonia, this technology is used in relation with electronic identity (ID card, mobile ID, digital ID). All members of X-Road are using Digital seal certificates for signing messages. Citizens and officials are using electronic identity tokens.
All participants must be implemented three-level IT baseline security system ISKE (https://www.ria.ee/en/iske-en.html). The goal of implementing ISKE is to ensure a security level sufficient for the data processed in IT systems. The necessary security level achieved by implementing the standard organisational, infrastructural/physical and technical security measures.
Data guidelines of Estonian Data Protection Inspectorate (http://www.aki.ee/et/juhised) must followed.
Benefits
Allows databases to interact, making integrated e-services possible
Institutions not locked into any one type of database or software provider
Factsheets 2016: 246 registers, 975 institutions, 1789 services, about 52000 organizations as indirect users, 575 million queries.
Last year the X-Road saved 656* years of working time. Assuming that every request saves 15 minutes and 4% of requests submitted via the X-Road involve communication between people, then using e-services helped save 5,745,810 working hours in previous year.
• personal code for citizens,
• code of institution,
• standardised address presentation.
Information regarding the X-Road members and the services they provide is available via the Administration System for the State Information System (RIHA). RIHA (https://www.ria.ee/en/administration-system-of-the-state-information-system.html ) serves as a catalogue for the state’s information system. At the same time RIHA is a procedural and administrative environment via which the comprehensive and balanced development of the state’s information system has ensured. RIHA guarantees the transparency of the administration of the state’s information system and helps to plan the state’s information management.
PKI or the public key infrastructure (https://www.ria.ee/en/public-key-infrastructure.html ) enables secure digital authentication and signing. The infrastructure also allows forwarding data by using an encrypting key pair: a public encryption key and a private decryption key. In Estonia, this technology is used in relation with electronic identity (ID card, mobile ID, digital ID). All members of X-Road are using Digital seal certificates for signing messages. Citizens and officials are using electronic identity tokens.
All participants must be implemented three-level IT baseline security system ISKE (https://www.ria.ee/en/iske-en.html). The goal of implementing ISKE is to ensure a security level sufficient for the data processed in IT systems. The necessary security level achieved by implementing the standard organisational, infrastructural/physical and technical security measures.
Data guidelines of Estonian Data Protection Inspectorate (http://www.aki.ee/et/juhised) must followed.
Benefits
Allows databases to interact, making integrated e-services possible
Institutions not locked into any one type of database or software provider
Factsheets 2016: 246 registers, 975 institutions, 1789 services, about 52000 organizations as indirect users, 575 million queries.
Last year the X-Road saved 656* years of working time. Assuming that every request saves 15 minutes and 4% of requests submitted via the X-Road involve communication between people, then using e-services helped save 5,745,810 working hours in previous year.
Citizen-centred design
X-Road is hided for end users
DATA HANDLING / DATA EXCHANGE
Type of data sharing
Actual data
Data handler
Stakeholder name
Information System Authority
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data provider
Kind of data
All types of data
Stakeholder name
Citizens
Stakeholder category
Citizen
Stakeholder Role
Data consumer
Kind of data
All types of data
Stakeholder name
Business
Stakeholder category
Business
Stakeholder Role
Data consumer
Kind of data
All types of data
Stakeholder name
Actors of the public administration
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data consumer
Kind of data
All types of data
Stakeholder name
Base registers
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data provider
Kind of data
All types of data
Stakeholder name
Secondary registers
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data provider
Kind of data
All types of data
Stakeholder name
Front end systems
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data consumer
Kind of data
All types of data
Stakeholder name
Front end systems
Stakeholder category
Business
Stakeholder Role
Data consumer
Kind of data
All types of data
Stakeholder name
Portals, citizen portal
Stakeholder category
Government
Stakeholder Role
Data consumer
Kind of data
All types of data
Architecture
One of the key elements of e-Estonia is that its databases are decentralized, which means:
• There’s no single owner or controller
• Every government agency or business can choose the product that’s right for them
• Services can be added one at a time, as they’re ready
X-Road is the all-important connection between these databases, the tool that allows them to work together for maximum impact. All of the Estonian e-solutions that use multiple databases use X-Road. All outgoing data from the X-Road is digitally signed and encrypted. All incoming data is authenticated and logged.
Originally X-Road was a system used for making queries to the different databases. Now it has developed into a tool that can also write to multiple databases, transmit large data sets and perform searches across several databases.
X-Road is a system that ensures secure and direct data exchange between its members.
During data exchange, X-Road ensures its parties with:
• Autonomy – an X-Road member defines, which data services it wishes to render and who gains access rights to the services;
• Confidentiality – information reaches only the authorized parties;
• Evidential value – using a digital signature enables proving the source of received data;
• Interoperability – all X-Road members speak the same language, regardless of the technology or architecture a member is using.
X-Road consists of:
• legal structure;
• organizational structure;
• protocol stack;
• software realizing the protocol stack.
The legal and organizational structure of X-Road regulates the following:
• who can or must be members of X-Road and how;
• scope of partial liabilities, rights and obligations.
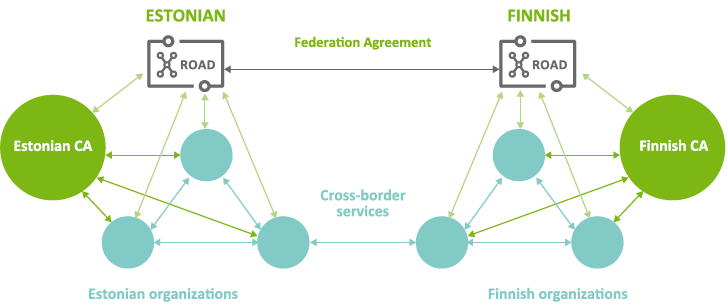
X-Road federation
The X-Road federation is the capability of X-Road to provide secure Internet-based data exchange across ecosystems (states) to members that belong in different ecosystems.
The X-Road federation is a situation, where there are similar X-Road environments in different states (or other organizations). Every X-Road environment managed by a competent organization (centre) that defines the applied security policy and manages the information of its ecosystem members.
For cross-border data services to exist, the X-Road centres need to conclude a federation agreement that entails the description of organizational and legal liabilities between the centres of different states.
X-Road members that have joined the X-Road environment in their state (centre) are able to exchange data (cross-border e-services) with the X-Road members in other states.
• There’s no single owner or controller
• Every government agency or business can choose the product that’s right for them
• Services can be added one at a time, as they’re ready
X-Road is the all-important connection between these databases, the tool that allows them to work together for maximum impact. All of the Estonian e-solutions that use multiple databases use X-Road. All outgoing data from the X-Road is digitally signed and encrypted. All incoming data is authenticated and logged.
Originally X-Road was a system used for making queries to the different databases. Now it has developed into a tool that can also write to multiple databases, transmit large data sets and perform searches across several databases.
X-Road is a system that ensures secure and direct data exchange between its members.
During data exchange, X-Road ensures its parties with:
• Autonomy – an X-Road member defines, which data services it wishes to render and who gains access rights to the services;
• Confidentiality – information reaches only the authorized parties;
• Evidential value – using a digital signature enables proving the source of received data;
• Interoperability – all X-Road members speak the same language, regardless of the technology or architecture a member is using.
X-Road consists of:
• legal structure;
• organizational structure;
• protocol stack;
• software realizing the protocol stack.
The legal and organizational structure of X-Road regulates the following:
• who can or must be members of X-Road and how;
• scope of partial liabilities, rights and obligations.
X-Road federation
The X-Road federation is the capability of X-Road to provide secure Internet-based data exchange across ecosystems (states) to members that belong in different ecosystems.
The X-Road federation is a situation, where there are similar X-Road environments in different states (or other organizations). Every X-Road environment managed by a competent organization (centre) that defines the applied security policy and manages the information of its ecosystem members.
For cross-border data services to exist, the X-Road centres need to conclude a federation agreement that entails the description of organizational and legal liabilities between the centres of different states.
X-Road members that have joined the X-Road environment in their state (centre) are able to exchange data (cross-border e-services) with the X-Road members in other states.
Image upload
Benefits for involved actors
X-Road will save 904 working years per one year in Estonia,
Allows databases to interact, making integrated e-services possible
Institutions not locked into any one type of database or software provider
Factsheets 2016: 246 registers, 975 institutions, 2375 services, about 52000 organisations as indirect users, 575 million queries
Allows databases to interact, making integrated e-services possible
Institutions not locked into any one type of database or software provider
Factsheets 2016: 246 registers, 975 institutions, 2375 services, about 52000 organisations as indirect users, 575 million queries
Lessons learned
Enabler 1. Secure data exchange layer X-Road is the well proven component of Estonian IT infrastructure
Enabler 2. The unique personal identification code provide opportunity to merge personal data from different registers.
Enabler 3. The unique company commercial registry code provide opportunity to merge business data from different registers.
Enabler 4. Master data in registers must described in catalogue RIHA properly.
Barrier 1. Legal and organisational interoperability is crucial for implementation
Barrier 2. Achieving PPP takes time and effort but pays off
Barrier 3. Cross border X-Road can achieved by high level political support
Enabler 2. The unique personal identification code provide opportunity to merge personal data from different registers.
Enabler 3. The unique company commercial registry code provide opportunity to merge business data from different registers.
Enabler 4. Master data in registers must described in catalogue RIHA properly.
Barrier 1. Legal and organisational interoperability is crucial for implementation
Barrier 2. Achieving PPP takes time and effort but pays off
Barrier 3. Cross border X-Road can achieved by high level political support
